If you wear a retainer, you know how crucial it is to keep it clean. A dirty retainer can harbor bacteria, cause bad breath, and even lead to oral health issues. In recent years, ultrasonic retainer cleaners have gained popularity as a convenient and effective way to clean these dental devices. But a common question lingers: are ultrasonic retainer cleaners safe? Let’s dive into the details to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding How Ultrasonic Retainer Cleaners Work
Before we assess their safety, it’s important to understand how ultrasonic retainer cleaners function. These devices use ultrasonic waves—high-frequency sound waves beyond the range of human hearing—to create tiny bubbles in a cleaning solution through a process called cavitation. As these bubbles implode, they generate powerful micro-jets of liquid that dislodge dirt, plaque, bacteria, and food particles from the surface and hard-to-reach areas of your retainer.
Most ultrasonic cleaners designed for retainers operate at frequencies between 20,000 and 45,000 Hz. This range is considered effective for cleaning without being overly aggressive. The cleaning cycle typically lasts anywhere from 3 to 10 minutes, depending on the model and the level of dirt on the retainer.

The Safety of Ultrasonic Cleaners for Different Retainer Materials
One of the primary concerns about ultrasonic retainer cleaners is whether they can damage the retainer itself. Retainers are made from various materials, and their compatibility with ultrasonic cleaning varies:
- Acrylic Retainers: These are among the most common types of retainers. Acrylic is generally durable, and ultrasonic cleaners are safe for acrylic retainers when used as directed. The gentle yet effective cleaning action removes buildup without scratching or weakening the material. However, it’s important to avoid using harsh cleaning solutions that could degrade the acrylic over time.
- Wire Retainers (Hawley Retainers): Hawley retainers consist of an acrylic base with metal wires. The metal components are typically made from stainless steel or nickel-titanium, both of which are resistant to corrosion and damage from ultrasonic waves. The key is to ensure the wires are securely attached to the acrylic before cleaning—loose wires may become more dislodged, but this is a rare occurrence if the cleaner is used properly.
- Clear Plastic Retainers (Essix Retainers): Clear plastic retainers are thin and can be more delicate than acrylic or wire retainers. When used correctly, ultrasonic cleaners are safe for Essix retainers. However, prolonged exposure to high-frequency waves or using a cleaner with too high a frequency could potentially cause the plastic to become brittle over time. It’s best to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning time and frequency.
- Lingual Retainers: These are permanently bonded to the back of the teeth, so they aren’t removed for cleaning. As a result, they don’t require ultrasonic cleaning, but if you have a removable retainer in addition to a lingual one, the same safety considerations apply as with other removable types.
In general, most retainer manufacturers approve of ultrasonic cleaning when used as instructed. However, if you’re unsure about your specific retainer, it’s always a good idea to check with your orthodontist.
Potential Risks and How to Mitigate Them
While ultrasonic retainer cleaners are generally safe, there are some potential risks to be aware of, along with steps to mitigate them:
- Damage from Over-Cleaning: Leaving your retainer in the ultrasonic cleaner for too long can increase the risk of damage, especially for delicate materials like clear plastic. Follow the recommended cleaning time—usually 3 to 5 minutes for regular cleaning. Avoid running multiple cycles in a row unless the retainer is extremely dirty, and even then, take short breaks between cycles.
- Harmful Cleaning Solutions: Some people make the mistake of using harsh chemicals like bleach, alcohol, or abrasive cleaners in their ultrasonic devices. These substances can damage the retainer material and may leave residue that’s harmful if ingested. Instead, use a mild, pH-neutral denture or retainer cleaning solution, or simply warm water with a small amount of gentle dish soap. Many ultrasonic cleaner manufacturers also sell specialized cleaning tablets designed for use with their devices.
- Cross-Contamination: If you use the ultrasonic cleaner for other items (like jewelry or dentures) in addition to your retainer, there’s a risk of cross-contamination. Bacteria from other items can transfer to your retainer, and vice versa. To avoid this, clean the ultrasonic tank thoroughly between uses, and consider designating the cleaner solely for your retainer if possible.
- Loosening of Components: For retainers with attached parts (like wires or clasps), the vibrations from the ultrasonic cleaner could potentially loosen these components over time, especially if they’re already worn or damaged. Inspect your retainer regularly for signs of wear, and if you notice any loose parts, stop using the ultrasonic cleaner and consult your orthodontist.
Impact on Oral Health: Is There a Risk?
Another concern is whether ultrasonic cleaning could pose a risk to your oral health. The good news is that when used properly, ultrasonic retainer cleaners are not harmful to your mouth. In fact, they can improve oral health by effectively removing bacteria and plaque that might otherwise cause gum irritation, cavities, or bad breath.
The cleaning solution used in the ultrasonic cleaner is a key factor here. Avoid using solutions that contain harsh chemicals, as they can irritate the gums or cause an unpleasant taste. After cleaning, always rinse your retainer thoroughly with warm water to remove any remaining cleaning solution before placing it back in your mouth.
There’s no evidence to suggest that the ultrasonic waves themselves have any negative impact on oral tissues. The waves are contained within the cleaning tank and do not come into contact with your mouth during the cleaning process.
Comparing Ultrasonic Cleaners to Other Cleaning Methods
To put the safety of ultrasonic retainers into perspective, let’s compare them to other common retainer cleaning methods:
- Brushing with Toothpaste: While brushing is a simple and effective method, using regular toothpaste can be abrasive and may scratch the surface of your retainer over time, creating tiny crevices where bacteria can hide. Ultrasonic cleaners, on the other hand, clean without abrasion.
- Soaking in Mouthwash: Some people soak their retainers in mouthwash, but many mouthwashes contain alcohol or other chemicals that can damage retainer materials, especially with repeated use. Ultrasonic cleaning with a mild solution is gentler.
- Denture Tablets: These are a popular alternative to ultrasonic cleaners. They work by releasing chemicals that dissolve plaque and kill bacteria. However, they may not be as effective at reaching deep crevices as ultrasonic waves. Also, some tablets contain bleach, which can discolor retainers.
- UV-Cleaning Devices: UV cleaners use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria. While they’re effective at disinfection, they don’t remove physical debris like plaque or food particles. Ultrasonic cleaners, by contrast, remove both debris and bacteria, making them a more comprehensive cleaning solution.
When compared to these methods, ultrasonic cleaners stand out for their effectiveness and safety when used correctly.
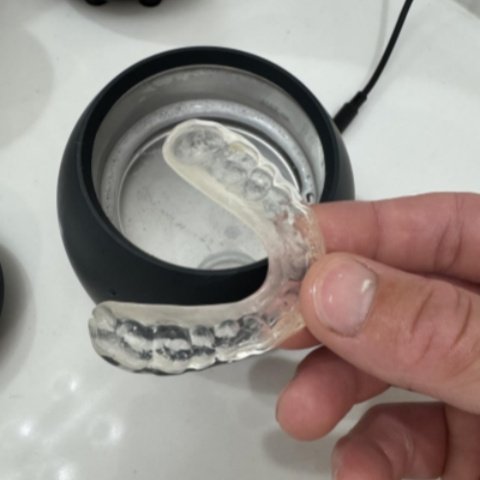

Tips for Safe and Effective Use of Ultrasonic Retainer Cleaners
To ensure you get the most out of your ultrasonic retainer cleaner while keeping it safe, follow these tips:
Read the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Every ultrasonic cleaner is slightly different, so familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines for your model, including recommended frequency, cleaning time, and compatible cleaning solutions.
Use the Right Solution: Stick to mild, retainer-safe cleaning solutions. Avoid bleach, alcohol, and abrasive cleaners. If you’re unsure, opt for warm water with a drop of gentle dish soap.
Don’t Overdo It: Clean your retainer with the ultrasonic cleaner 2-3 times a week for regular maintenance. Daily cleaning with a soft toothbrush and mild soap is usually sufficient, with ultrasonic cleaning as a deeper clean.
Inspect Your Retainer Regularly: Check for signs of damage like cracks, chips, or loose wires before and after each ultrasonic cleaning. If you notice any issues, stop using the cleaner and contact your orthodontist.
Clean the Ultrasonic Tank: After each use, empty the cleaning solution, rinse the tank with warm water, and wipe it dry to prevent the buildup of bacteria or mineral deposits.
Store Your Retainer Properly: When not in use, keep your retainer in a clean, dry case to prevent contamination. Avoid leaving it in direct sunlight or hot environments, as heat can warp the material.
Expert Opinions: What Dentists and Orthodontists Say
Most dental professionals agree that ultrasonic retainer cleaners are safe when used appropriately. Dr. Sarah Johnson, a practicing orthodontist with over 15 years of experience, notes, “I often recommend ultrasonic cleaners to my patients because they do a great job of removing plaque and bacteria from hard-to-reach areas. The key is to use them as directed—don’t over-clean, and use a gentle cleaning solution. In my practice, I’ve rarely seen damage to retainers from ultrasonic cleaners when patients follow the guidelines.”
Dr. Michael Chen, a dentist who specializes in preventive care, adds, “Ultrasonic cleaning is a safe and effective method for maintaining retainers. It’s much more thorough than brushing alone, which can help prevent oral health issues down the line. As long as patients are careful not to use harsh chemicals and don’t leave the retainer in too long, there’s little risk of damage.”
Conclusion: Are Ultrasonic Retainer Cleaners Safe?
After examining the evidence, it’s clear that ultrasonic retainer cleaners are safe for most retainers when used correctly. They provide a thorough clean that helps maintain both the retainer’s condition and your oral health. The key factors to ensure safety are: using the right cleaning solution, following the recommended cleaning time, inspecting your retainer regularly for damage, and avoiding over-use.
As with any dental care product, it’s important to use common sense and consult your orthodontist if you have any concerns about your specific retainer. With proper use, an ultrasonic retainer cleaner can be a valuable tool in keeping your retainer clean, your mouth healthy, and your smile bright.…









 chair holds up to 330 lbs (150 kg). Ergonomic lumbar support helps reduce fatigue by up to 42% after three hours of use which adopts
chair holds up to 330 lbs (150 kg). Ergonomic lumbar support helps reduce fatigue by up to 42% after three hours of use which adopts